
- JRIVER MEDIA CENTER WINDOWS 7 BIT PERFECT FULL
- JRIVER MEDIA CENTER WINDOWS 7 BIT PERFECT SOFTWARE
- JRIVER MEDIA CENTER WINDOWS 7 BIT PERFECT SERIES
apply lots of random volume changes JRDoubleArray aryDecibelChanges for (int i = 0 i 1.0) ? JRMath::GetRandomNumber(0.0f, -100.0f) : JRMath::GetRandomNumber(0.0f, 100.0f) dValue *= CDecibels::GetMultiplierFromDecibels(dDecibelsChange) aryDecibelChanges.Choosing the right audiophile playback software can be a daunting task. take a snapshot of the value at 32-bit (the highest used bitdepth of any hardware most high-end hardware is 24-bit) int nValue32Bit1 = CConvertFromFloatToInteger::Convert(dValue) constants const int nIterations = 100 * MILLION // apply lots of volume changes double dValue = 0.9323402123 // starting value (doesn't really matter what value we choose since it changes by huge random amounts) It's provided here for completeness sake, and to show that the information above is based on real-world, repeatable, results. It's only interesting if you are a programmer. This is the proof of the example listed above. This does not mean that the file has improved, only that Media Center does the best job possible dealing with the MP3 (or other lossy) data that is not inherently precise to some number of bits.
In other words, taking a 16bit input file, encoding as MP3, and then playing it in Media Center will cause 64bit data to be delivered to the playback engine.
JRIVER MEDIA CENTER WINDOWS 7 BIT PERFECT FULL
Media Center preserves the full 64bit precision when converting from the lossy format to PCM and uses as much precision as possible during output. There is no true or correct bitdepth in this case.
Lossy formats like MP3 use floating point math to build their output values.
JRIVER MEDIA CENTER WINDOWS 7 BIT PERFECT SERIES
This also means one volume change or a series of 100 million volume changes that add up to the same net result is bit-identical. In other words, this incredible number of changes results in a bit-perfect output at 32bit, which is the highest hardware output bitdepth (most high-end hardware is 24bit). To demonstrate the incredible precision of 64bit audio, imagine applying 100 million random volume changes (huge changes from -100 to 100 dB), and then applying those same 100 million volume changes again in the opposite direction.Īmazingly, you will have the exact same signal at 32bit after 200 million huge volume changes as when you started. In other words, it is bit-perfect on all known hardware. The precision offered by Media Center's 64bit audio engine is billions of times greater than the best hardware can utilize. In other words, the ASIO framework (which is very good) has the advice above about using the highest bitdepth available built in. This is because ASIO automatically delivers audio to the soundcard in the highest bitdepth that it supports. If you use ASIO, the output bitdepth selection is ignored.
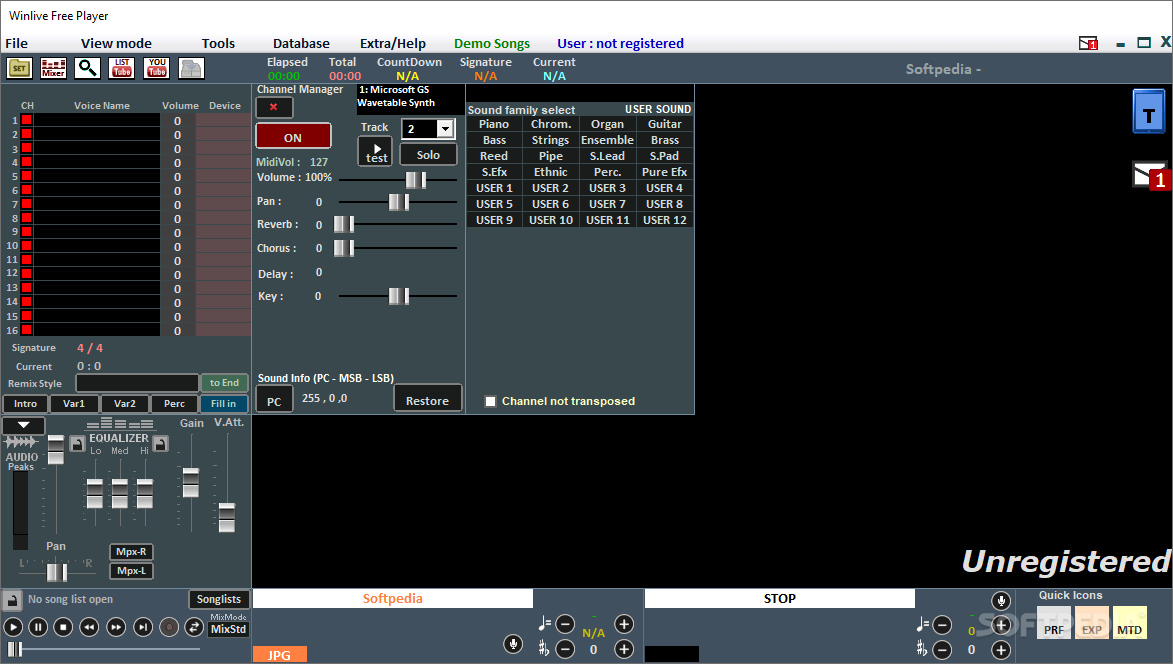
For example, the number "10" might become "10.0" or "10.00" if you add more bits, but all three representations are perfectly identical. Conceptually, imagine adding bits like adding zeroes at the end of a decimal. Each bit is worth 6dB, so:Ĭonverting from less bits to more bits is perfectly lossless. It's also possible to represent the bitdepth in decibels. This means each measurement of the sound wave will have one of 65536 (2^16) values.Ī good DAC is 24bit, meaning each measurement will have one of 16777216 (2^24) values. This is where the name bitdepth comes from.īitdepth describes the number of 0's or 1's (computers are binary) used for each height measurement of the sound wave.įor example, an audio CD is 16bit. One common unit in digital audio, and the unit used inside Media Center, is bits. There are several ways to describe the precision used for measuring the height of the sound wave.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
